As the world accelerates its transition to a low-carbon economy, carbon credits have become a cornerstone of corporate and national climate strategies. In 2026, the carbon credit market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by regulatory pressures, corporate net-zero commitments, and a surge in demand for high-integrity offsets. This article explores the latest carbon credit prices, key market trends, and what businesses need to know to navigate this evolving landscape.
What Are Carbon Credits and Why Do Prices Matter?
Carbon credits represent one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases that have been reduced, removed, or avoided. These credits are traded in two main markets: compliance (mandatory systems like the EU Emissions Trading System) and voluntary (where companies and individuals purchase credits to offset emissions beyond regulatory requirements).
Price transparency is crucial because it directly impacts the cost of compliance for businesses and the viability of carbon reduction projects. For companies aiming to meet sustainability goals, understanding price dynamics helps in budgeting, risk management, and strategic decision-making.
Current Carbon Credit Prices (2026)
Voluntary Carbon Market
Nature-based credits (e.g., afforestation, reforestation): Prices range from $7 to $24 per ton, with premium projects reaching up to $21.3 per ton.
Technology-based removals (e.g., direct air capture): Prices can exceed $170–$500 per ton due to higher costs and limited supply.
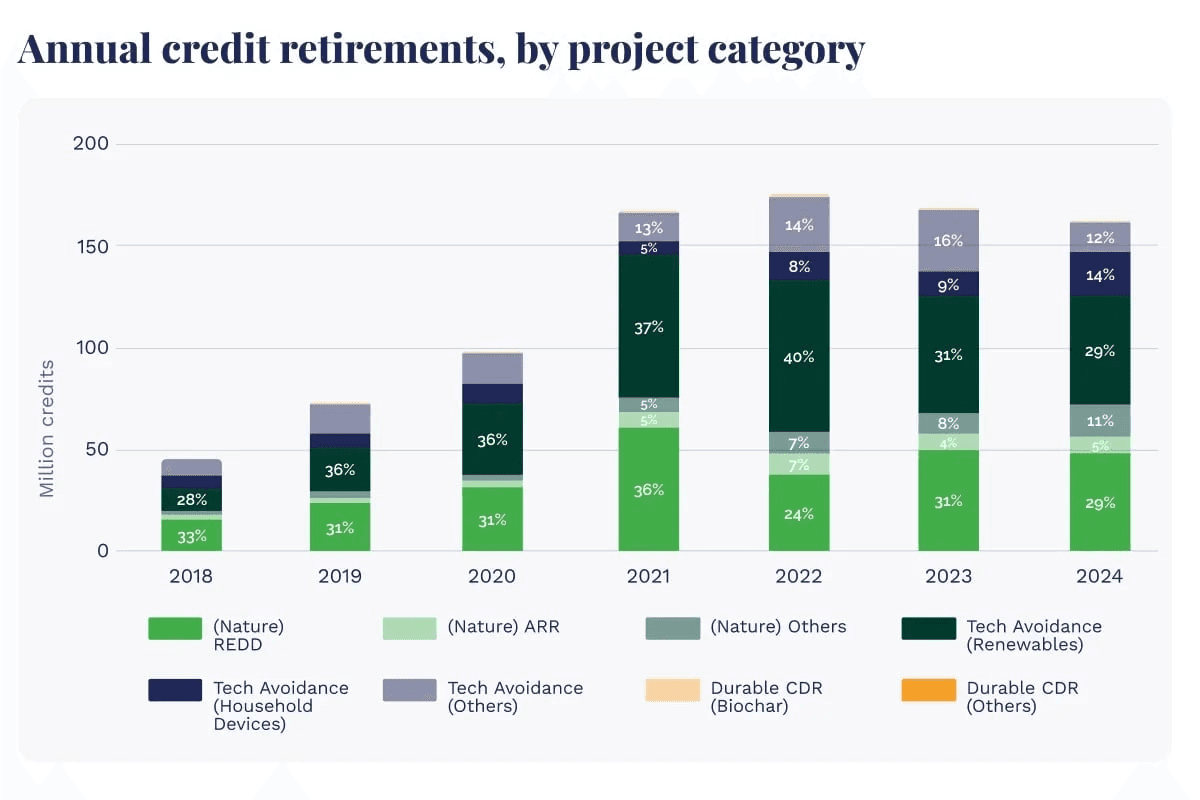
Average prices: The voluntary market saw a record 95 million credits retired in the first half of 2025, with high-rated credits trading at more than 300% above lower-rated ones.
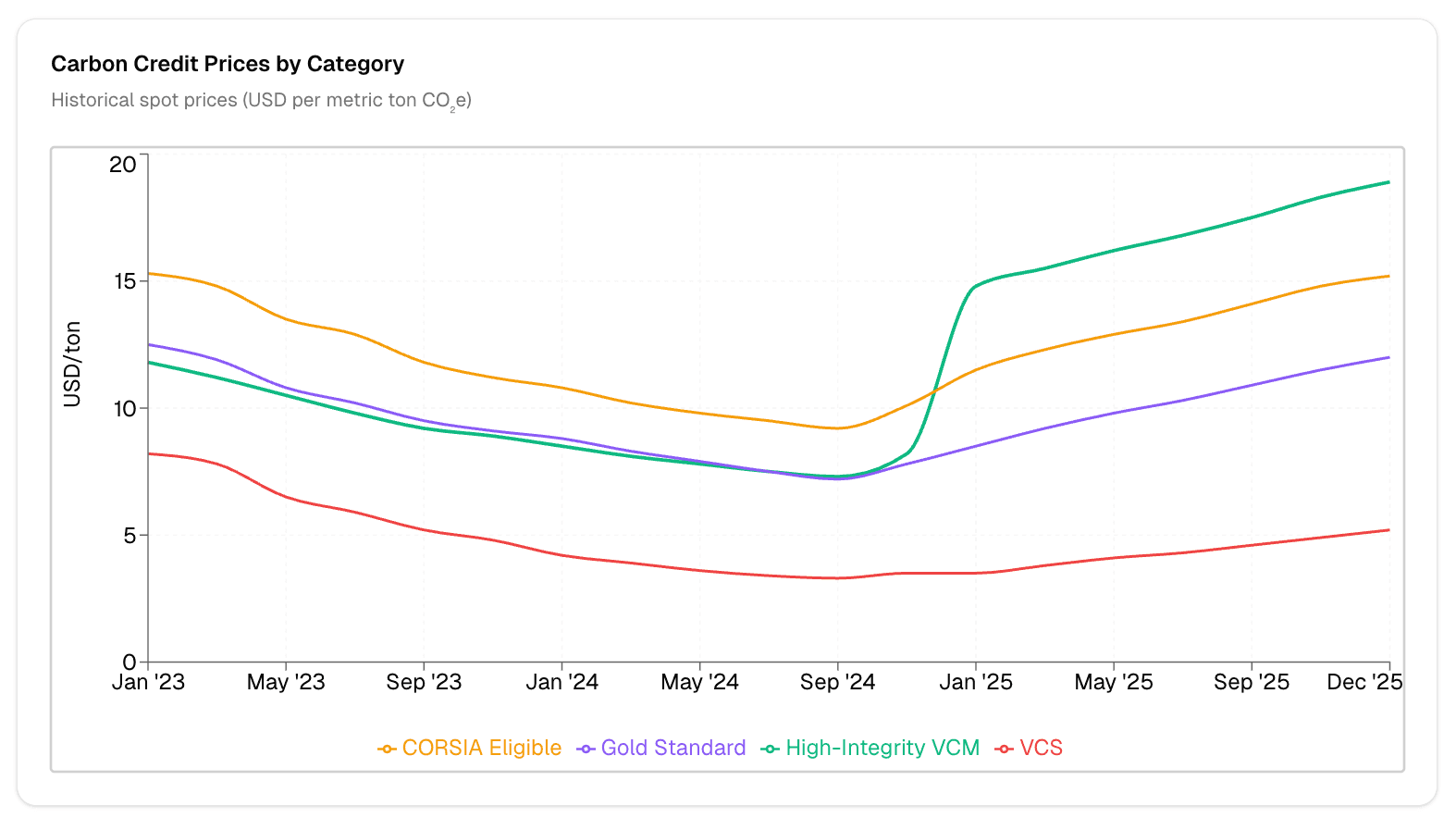
Compliance Carbon Market
EU Carbon Permits: Rose to 82.85 EUR ($89) per ton in December 2025, up 21.52% year-over-year.
Global average: Compliance markets cover about 28% of global emissions, with average prices around $19 per ton.
Key Factors Influencing Carbon Credit Prices
Several factors shape carbon credit pricing in 2025:
Market Supply and Demand: Increased corporate sustainability budgets and regulatory mandates are driving demand, while supply remains constrained for high-quality credits.
Project Type and Quality: Nature-based projects dominate (46% of demand), but technology-based removals command premium prices due to their permanence and scalability.
Regulatory Landscape: New standards like the ICVCM’s Core Carbon Principles and updates to Article 6 of the Paris Agreement are raising the bar for credit integrity.
Geopolitical and Economic Factors: Inflation, geopolitical instability, and project implementation costs influence pricing.
Certification Standards: Credits from recognized standards (e.g., Verra, Gold Standard) are priced higher due to perceived reliability.
Historical Trends and Price Charts
Price Evolution (2020–2025)
2020–2022: Steady price increases as corporate net-zero pledges surged.
2023–2024: Prices dipped due to concerns over credit quality and transparency.
2025: Rebound driven by stricter regulations and a focus on high-integrity projects.
Source: ClimateSeed Comparison of Carbon Credits
Compliance vs. Voluntary Markets
Compliance markets are larger and more stable, with prices tied to regulatory caps.
Voluntary markets are more volatile but offer flexibility and innovation in project types.
Voluntary vs. Compliance Carbon Markets
Feature | Voluntary Market | Compliance Market |
|---|---|---|
Participation | Voluntary, open to all | Mandatory for regulated industries |
Price Drivers | Corporate sustainability goals, brand value | Regulatory caps, penalties |
Project Types | Diverse (nature-based, tech-based) | Focused on regulated sectors |
Standards | Verra, Gold Standard, Plan Vivo | Government-led (e.g., EU ETS, CORSIA) |
Price Range (2025) | $7–$500 per ton | $19–$89 per ton |
For a deeper dive, read Regreener’s guide on voluntary and compliance markets .
Forecast for 2026 and Beyond
Short-Term (2026–2030)
Price trends: Average carbon prices are expected to rise to $30 per ton by 2040, with nature-based credits leading the growth.
Market size: The voluntary carbon market is projected to grow at a 20.59% CAGR, reaching $16.38 billion by 2035.
Supply outlook: BloombergNEF forecasts supply to surge 20- to 35-fold by 2050, driven by nature-based and technology-based solutions.
Long-Term (2030–2050)
Technology-based removals will play a larger role as costs decrease and scalability improves.
Regulatory integration: Compliance markets may increasingly accept high-quality voluntary credits, boosting demand.
Source: BloombergNEF Long-Term Carbon Credit Supply Outlook
The Size and Growth of the Voluntary Carbon Market
The voluntary carbon market has experienced remarkable growth in recent years, reflecting the increasing urgency of global climate action and the rising number of corporate net-zero commitments. In 2025, the market is valued at approximately $2.52 billion, with projections indicating it will expand to $3.04 billion in 2026 and reach $16.38 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.59%.
This expansion is driven by stronger ESG reporting requirements, heightened climate accountability, and a growing preference for nature-based projects, which currently account for nearly half of all voluntary carbon credit demand. As more companies integrate carbon credits into their decarbonization roadmaps—whether to offset residual emissions, enhance brand reputation, or meet stakeholder expectations—the market is set to become a cornerstone of corporate sustainability strategies.
With over 58% of carbon credit buyers prioritizing projects that deliver ecological co-benefits, such as biodiversity conservation and community upliftment, the voluntary market is not only growing in size but also evolving in scope, offering diverse solutions to address the climate crisis.
How Businesses Can Navigate Carbon Credit Markets
Best Practices for Procurement
Prioritize high-integrity credits: Focus on projects with robust additionality, permanence, and co-benefits.
Diversify portfolios: Balance nature-based and technology-based credits to manage risk and cost.
Stay informed: Monitor regulatory changes and market trends to anticipate price movements.
Avoid greenwashing: Ensure credits align with science-based targets and avoid double-counting.
To learn more about how your company can use carbon credits, explore Regreener’s case studies.
Conclusion
Carbon credit prices in 2025 reflect a maturing market with growing demand for transparency and quality. Businesses that stay ahead of trends, prioritize high-integrity credits, and integrate carbon offsets into broader decarbonization strategies will be best positioned to meet their climate goals.
For tailored advice on carbon credit procurement, contact Regreener’s experts or explore our carbon credit services.
Common Questions About Carbon Credit Prices
What determines the price of a carbon credit?
Prices are influenced by project type, location, certification standard, and market demand.
How can businesses ensure they are buying high-quality credits?
Look for credits certified by Verra, Gold Standard, or similar bodies, and verify additionality and permanence.
What is the best time to buy carbon credits?
Monitor market trends and regulatory updates. Purchasing during periods of lower demand can yield better prices.






