Introduction
Europe is leading the global transition to a sustainable future, with ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 and achieve climate neutrality by 2050. As part of this commitment, the European Union is fostering innovative carbon credit projects that not only offset emissions but also drive sustainable development, restore ecosystems, and support local communities.
In this article, we highlight the five best EU carbon credit projects of 2026, selected for their measurable impact, additionality, and alignment with the EU Green Deal and United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Whether you’re a business aiming to meet net-zero goals or an individual passionate about climate action, these projects offer high-integrity opportunities to make a tangible difference.
What is a Carbon Credit?
A carbon credit represents one metric ton of carbon removed from the atmosphere or prevented from being emitted. These credits are generated by projects that reduce, avoid, or sequester emissions—such as reforestation, renewable energy, regenerative agriculture, or carbon capture technologies. By purchasing carbon credits, companies, governments, and individuals can finance sustainable development while compensating for their own emissions.
In the EU, carbon credits play a crucial role in supporting the bloc’s climate ambitions. The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) remains the world’s largest compliance market, while the voluntary carbon market (VCM) is rapidly expanding, driven by corporate sustainability commitments and regulatory incentives. For a deeper understanding of how carbon credits work, visit Regreener’s carbon credits FAQ.
Why Focus on EU Carbon Credit Projects?
The European Union is a global leader in climate innovation, with a strong focus on circular economy principles, renewable energy, and nature-based solutions. EU carbon projects stand out for several reasons:
Innovation: The EU is home to cutting-edge technologies in carbon farming, reforestation, and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Scalability: EU projects often benefit from cross-border collaboration, EU funding, and advanced infrastructure, making them scalable and impactful.
Co-Benefits: Many projects deliver additional benefits, such as improving biodiversity, supporting local economies, and enhancing social equity.
By supporting EU carbon projects, buyers can contribute to both global climate goals and local sustainability efforts.
Regulation and the EU Climate Goals
The EU’s climate policy framework is among the most ambitious in the world. The EU Green Deal aims for climate neutrality by 2050, with intermediate targets to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030. The Fit for 55 Package accelerates this transition by reforming the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS), introducing the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), and setting new standards for carbon removals.
A landmark development is the EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework (CRCF), which establishes strict criteria for carbon removal projects. This framework ensures transparency, additionality, and permanence, boosting investor confidence and setting a global benchmark for carbon credit integrity. The CRCF is particularly significant as it aligns voluntary and compliance markets, ensuring that projects contribute meaningfully to the EU’s climate goals.
The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) is the world’s largest compliance carbon market, covering over 11,000 power plants and industrial installations. While the ETS primarily focuses on compliance, the voluntary carbon market (VCM) is expanding rapidly, driven by corporate net-zero pledges and demand for high-quality credits. The EU’s regulatory environment ensures that both markets operate with integrity, making EU carbon credits a trusted choice for businesses and individuals alike.
EU carbon market and its Development
The EU carbon market is supported by robust certification bodies and standards, ensuring that projects meet the highest environmental and social integrity criteria. Key players include:
Gold Standard: Certifies projects with a focus on sustainable development and social impact, ensuring that carbon credits deliver real, measurable benefits.
Puro.earth: Specializes in carbon removal projects, offering a transparent and standardized approach to certifying engineered and nature-based solutions.
Market Growth and Development
The EU carbon market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by corporate net-zero commitments, regulatory incentives, and increasing demand for high-integrity credits. The voluntary carbon market (VCM) in Europe is expanding as companies seek to offset unavoidable emissions while contributing to sustainable development. This growth is supported by EU funding programs such as Horizon Europe, the LIFE Programme, and the Innovation Fund, which provide grants, technical assistance, and pilot projects for innovative carbon removal and reduction technologies.
The market is diversifying, with a surge in nature-based solutions (e.g., reforestation, peatland restoration, and agroforestry) and technology-based removals (e.g., direct air capture, biochar, and enhanced weathering). Cross-border collaborations and public-private partnerships are also emerging, fostering scalable and impactful projects. As the EU strengthens its regulatory framework, the market is becoming more transparent, attracting both institutional and retail investors. This dynamic environment positions Europe as a global leader in carbon credit innovation, setting benchmarks for quality and impact.
The 5 Best EU Carbon Credit Projects of 2026
1. LIFE Carbon Farming Initiative – Spain, Italy, and France

Overview
The LIFE Carbon Farming Initiative is a transnational project supported by the EU LIFE Programme, encouraging farmers to adopt practices that reduce their carbon footprint and increase carbon storage in soils and vegetation. Over six years, 700 farms across six European countries aim to achieve a 15% reduction in their carbon footprint by 2027.
Location: Spain, Italy, France, and other EU countries.
Annual Impact: Thousands of tons of carbon sequestered annually, with additional benefits for soil health and biodiversity.
Key Benefits
Climate: Enhances carbon storage in agricultural soils and reduces emissions from farming activities.
Community: Provides farmers with financial incentives and technical support to transition to sustainable practices.
Biodiversity: Improves soil health and supports pollinators and other wildlife.
SDGs: Aligns with SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 13 (Climate Action), and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Why It Stands Out
The LIFE Carbon Farming Initiative is one of the largest and most ambitious carbon farming projects in the EU. By involving hundreds of farms across multiple countries, it demonstrates the scalability of carbon farming as a climate solution. The project’s focus on regenerative agriculture—such as cover cropping, reduced tillage, and agroforestry—ensures long-term carbon sequestration while improving farm resilience. Its integration with the EU Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) further strengthens its impact, making it a model for future carbon farming initiatives in Europe.
2. Baltic Sea Blue Carbon – Estonia and Finland

Overview
The Baltic Sea Blue Carbon project focuses on restoring coastal wetlands and seagrass meadows in the Baltic Sea region. These ecosystems are among the most effective natural carbon sinks, sequestering carbon at rates up to 50 times faster than tropical rainforests.
Location: Coastal areas of Estonia and Finland.
Annual Impact: Hundreds of tons of carbon sequestered annually, with co-benefits for marine biodiversity and water quality.
Key Benefits
Climate: Coastal wetlands and seagrass meadows sequester large amounts of carbon in sediments and biomass.
Community: Supports local fisheries and tourism by improving coastal ecosystem health.
Biodiversity: Restores habitats for fish, birds, and marine mammals.
SDGs: Aligns with SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Why It Stands Out
Blue carbon ecosystems are critically underrepresented in global carbon markets, despite their outsized potential for carbon sequestration. This project is pioneering in its focus on the Baltic Sea, a region with unique ecological challenges and opportunities. By combining wetland restoration with community engagement, the project ensures long-term success and sets a precedent for blue carbon initiatives across Europe. Its certification under Verra’s VCS guarantees transparency and additionality, making it a trusted choice for buyers.
3. Carpathian Reforestation – Romania

Overview
The Carpathian Reforestation project aims to restore degraded forests in Romania’s Carpathian Mountains, one of Europe’s last wilderness areas. The project focuses on planting native tree species to enhance biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
Location: Carpathian Mountains, Romania.
Annual Impact: Tens of thousands of tons of carbon sequestered annually, with long-term benefits for forest resilience.
Key Benefits
Climate: Forests act as carbon sinks, removing carbon from the atmosphere for decades.
Community: Creates jobs in forestry and eco-tourism, supporting rural economies.
Biodiversity: Restores habitats for endangered species like the Eurasian lynx and brown bear.
SDGs: Aligns with SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Why It Stands Out
The Carpathian Mountains are a biodiversity hotspot, and this project is one of the largest reforestation efforts in Eastern Europe. By focusing on native species and natural regeneration, the project ensures ecological integrity and long-term carbon storage. Its partnership with local communities and conservation NGOs guarantees that benefits are shared equitably, making it a model for community-led reforestation. The project is certified under the Gold Standard, ensuring high environmental and social integrity.
4. Icelandic Carbon Mineralization – Iceland

Overview
The Icelandic Carbon Mineralization project leverages the country’s unique geology to permanently store carbon by turning it into stone. Carbon dioxide is injected into basaltic rock formations, where it mineralizes within two years, providing a permanent and secure storage solution.
Location: Hellisheiði, Iceland.
Annual Impact: Thousands of tons of carbon mineralized annually, with potential for significant scaling.
Key Benefits
Climate: Offers permanent carbon storage, addressing concerns about reversibility in other carbon removal methods.
Innovation: Demonstrates the feasibility of carbon mineralization as a large-scale climate solution.
Community: Supports Iceland’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
SDGs: Aligns with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Why It Stands Out
Carbon mineralization is one of the most promising permanent carbon removal technologies. This project, operated by Carbfix, is the world’s first commercial-scale mineralization facility. Its success has attracted global attention, with potential applications in other volcanic regions. The project’s permanence and scalability make it a standout choice for corporations seeking high-integrity carbon removal solutions. It is also one of the few projects certified under Puro.earth, a leading standard for carbon removal.
5. Climeworks Direct Air Capture (DAC) – Iceland
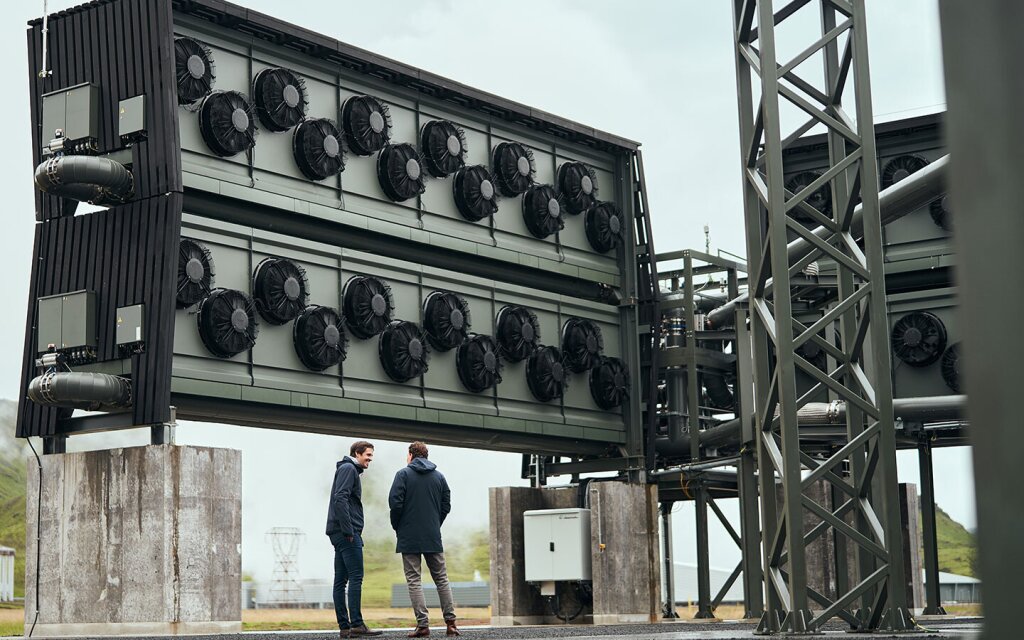

Overview
The Climeworks DAC Project in Iceland is one of Europe’s most advanced direct air capture facilities, designed to remove carbon directly from the atmosphere and permanently store it underground. Using renewable energy, the facility captures carbon and injects it into basaltic rock formations, where it mineralizes within two years, ensuring permanent storage.
Location: Hellisheiði, Iceland.
Annual Impact: Thousands of tons of carbon removed annually, with plans to scale up to megaton capacity by 2030.
Key Benefits
Climate: Direct air capture is one of the few technologies capable of removing carbon from the atmosphere at scale, making it essential for achieving net-zero goals.
Innovation: Demonstrates the feasibility of large-scale carbon removal using renewable energy.
Permanence: Carbon is permanently stored as stone, eliminating the risk of re-release.
SDGs: Aligns with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Why It Stands Out
Climeworks’ DAC facility in Iceland is a global pioneer in engineered carbon removal, offering a scalable and permanent solution for hard-to-abate emissions. Unlike nature-based solutions, DAC provides measurable, verifiable, and permanent carbon removal, making it ideal for corporations with ambitious net-zero targets. The project is powered entirely by geothermal energy, ensuring minimal environmental impact. Its certification under Puro.earth and alignment with the EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework (CRCF) make it a trusted choice for high-integrity carbon credits.
Project Name | Type | Annual Carbon Impact | Key SDGs | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LIFE Carbon Farming Initiative | Carbon Farming | Thousands of tons | 2, 13, 15 | Scalable, farmer-focused |
Baltic Sea Blue Carbon | Blue Carbon Restoration | Hundreds of tons | 13, 14, 15 | Pioneering coastal ecosystem restoration |
Carpathian Reforestation | Reforestation | Tens of thousands | 13, 15 | Biodiversity hotspot restoration |
Icelandic Carbon Mineralization | Carbon Mineralization | Thousands of tons | 9, 13 | Permanent carbon storage |
Climeworks DAC – Iceland | Direct Air Capture | Thousands of tons | 9, 13 | Engineered, permanent carbon removal |
How to Procure EU Carbon Credits
For organizations and individuals looking to invest in EU carbon projects, several pathways are available:
Direct Purchase: Buy credits directly from project developers or through reputable platforms like Regreener.
Expert Guidance: Work with advisors to tailor a carbon offsetting strategy to your needs. Contact Regreener for personalized advice.
Retirement: Once purchased, credits are retired in your name, ensuring transparency and preventing double-counting.
Tip: Diversify your portfolio by supporting multiple projects across different sectors and regions.
Risks and Considerations
Price Volatility
Carbon credit prices can fluctuate due to market demand, regulatory changes, or economic conditions. These fluctuations may impact long-term budgeting for offsetting strategies.
Reversals
Nature-based projects, such as reforestation or wetland restoration, are vulnerable to reversals from extreme weather, pests, or policy changes. To mitigate these risks, projects use buffer pools and rigorous monitoring.
Ethical Considerations
Carbon credits should complement—not replace—direct emissions reductions. Prioritize reducing your own carbon footprint before relying on offsets.
EU-Specific Challenges
The European Union faces a unique set of challenges in scaling carbon projects while maintaining environmental integrity and social equity. One of the most pressing issues is land-use competition, as the demand for carbon sequestration projects—such as reforestation, agroforestry, and wetland restoration—often conflicts with other priorities like agriculture, urban development, and renewable energy infrastructure. For example, large-scale reforestation initiatives may compete with food production, particularly in regions where arable land is limited. This tension requires careful planning and innovative solutions, such as agroforestry systems that combine tree planting with crop production, or restoring degraded lands that are no longer suitable for agriculture.
Another critical challenge is ensuring a just transition for communities and industries affected by the shift toward carbon-neutral economies. The EU’s climate policies, while essential for long-term sustainability, can disrupt traditional industries, such as coal mining or conventional agriculture. To address this, the EU must prioritize retraining programs, economic diversification, and social safety nets to ensure that no community is left behind. The Just Transition Fund, part of the EU’s broader climate strategy, is designed to support regions most affected by the green transition, but its success depends on effective implementation and local engagement.
Conclusion
The five projects highlighted above represent the best of EU carbon credit initiatives in 2026. By supporting these efforts, organizations and individuals can advance their climate goals while contributing to sustainable development, biodiversity, and local economies.
Ready to take the next step? Whether you’re looking to offset emissions, enhance your sustainability strategy, or explore high-integrity carbon projects, contact Regreener today to speak with our team and start your journey toward meaningful climate impact.